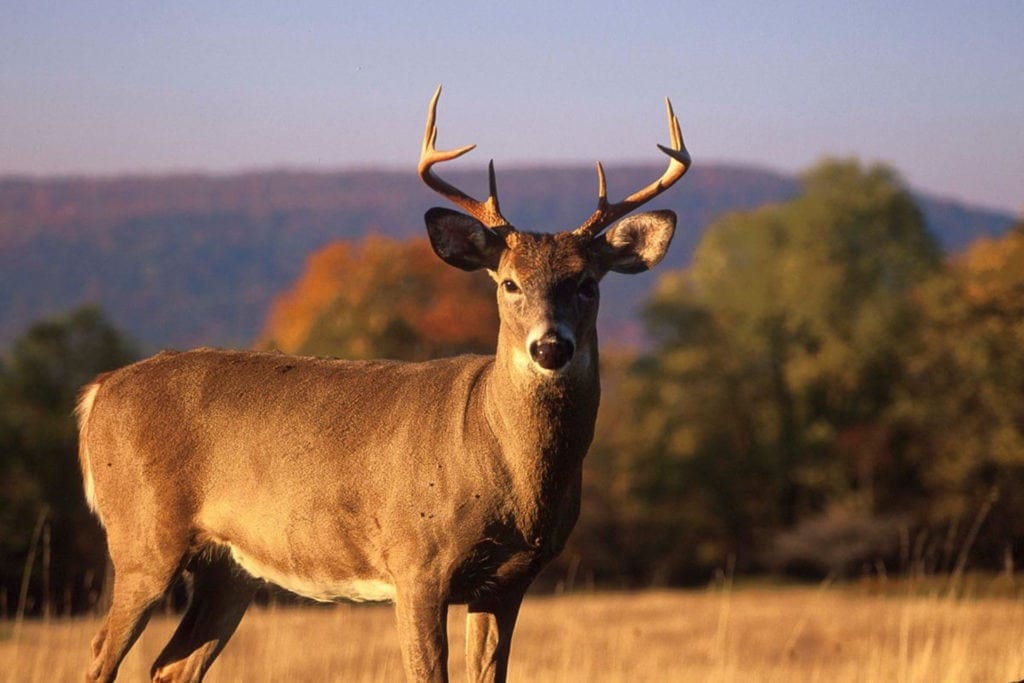
SOUTH CHARLESTON, W.Va. —West Virginia is experiencing an outbreak of Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease (EHD) in the state’s white-tailed deer herd, according to the Wildlife Resources Section of the West Virginia Division of Natural Resources (DNR).
So far this year, deer have been found dead in small areas of Summers, Monroe and Greenbrier counties. Epizootic Hemorrhagic Disease, virus serotype 2 (EHDV-2) has been isolated from Summers County. Hemorrhagic Disease can be caused by either EHDV or Blue Tongue Virus (BTV). No BTV infected deer have been detected.
West Virginia samples were sent to the Southeastern Cooperative Wildlife Disease Study located at the University of Georgia, School of Veterinary Medicine where they isolated and identified the virus as EHDV-2. Although this disease usually does not have a major impact on the deer population, the DNR Wildlife Resources Section is surveying the extent of the disease outbreak in the state. EHDV may cause local reductions in the deer herd of 20% or less.
“The disease disappears with the first frost, because the spread of the virus is dependent on small midges called Culicoides that are killed by cold temperatures,” said Gary Foster, assistant chief in charge of game management for DNR.
EHD does not occur in West Virginia every year; the last large outbreaks of this disease in West Virginia were in 1996, 2002, 2007, 2012, and 2017. EHDV does not persist in deer that survive infection.
“Although hunters should never consume an obviously sick deer, EHDV is not a reason for hunters to be concerned about consuming their deer,” Foster said.
This disease is not contagious to humans, and EHDV is not related to chronic wasting disease, which has only been detected in Berkeley, Hampshire, Hardy, Mineral and Morgan counties.
Landowners and hunters in the Summers, Monroe, and Greenbrier county region are urged to report sick or dead deer to the DNR District 4 Office located in Beckley at 304-256-6947. If landowners find sick or dead deer in other regions of the state, they should contact their appropriate DNR district office.